- What is the tertiary sector?
- Who provides the services?
- The trade
- International trade organizations
- Transport and communications
- The tertiary sector in Europe: The tertiaryization of the economy in Europe
What is the tertiary sector?
Economic activity is traditionally divided into three sectors: primary , secondary and tertiary .
The tertiary sector or service sector includes all activities that produce intangible goods and provide services to the population or companies . This definition includes essential services such as education and health, but also advertising, legal aid, cleaning and internet providers.
To approach its analysis, we divide it into several subsectors :
- Commerce , related to all the processes of distribution and sale of goods and products.
- Transport and communications , which include the movement of people and goods, as well as communication and information flows.
- Tourism , which includes the temporary displacement of the population for leisure purposes.
Since the end of the 20th century, and in the present century, the quaternary subsector has gained more weight and importance with activities linked to information and knowledge , such as information and communication technologies, consulting services, activities included in R +D+I and financial services.
This subsector is gaining so much weight in the economies of the most developed countries that some authors single it out as a new economic sector.
What is the relationship between employment by sector and economic development?
The active population works in one of the three sectors of economic activity. The resulting distribution is the structure of employment and reveals details of the economy of the country or area.
In the most developed countries around 70% of the population works in the tertiary sector , compared to a primary sector reduced to the maximum possible employing only 4%-6% of the active population. In contrast, countries with a lower level of development have a large volume of workers in the primary sector. Along with the active population, the contribution to a country’s GDP from each economic sector is related to the level of development: the higher the tertiary sector’s contribution to GDP, the higher the level of development.
Who provides the services?
One of the most common ways to classify services is based on who provides this service , dividing them into public and private services .
The State is the provider of public services that seek to guarantee the well-being of citizens through what we call basic services : health, education, defense and public order, etc.
Private services , managed by companies , have as their objective the financial benefit of these companies, such as banks.
There are exclusively private services, such as advertising and commerce. Others can be offered publicly and privately at the same time, such as health care, and it is the user who opts for one or the other, depending on their interests and financial solvency.
The welfare state
The provision of public services to citizens by the state is linked to the concept of the ” welfare state ” which was consolidated in European states during the 1940s. The difficult social conditions after the Second World War pushed the European governments to approve a set of social laws that created a ” social security” system that would protect the citizen and guarantee fair access to public services and the well-being of the population . Within these services, there are measures such as unemployment benefit, retirement pension, paid working holidays, health care, paid maternity/paternity leave, etc.
Although some of these measures existed since the late 19th century, they did not become widespread until the mid-20th century. This does not mean that conditions are the same in all countries of the world today; there are huge differences between developed and developing countries in terms of the welfare state. One of the ways to measure these inequalities is found in the HDI or Human Development Index , an indicator developed by the United Nations . In this index the maximum value is 1, so the closer a country’s value is to 1, the higher the quality of life and well-being of the population.
The trade
The products we use and consume every day are made in different places on the planet. It is the commercial activity that distributes them and brings them to our homes.
Commercial activity is the distribution of raw materials, goods and services, connecting producers and consumers. Commerce has evolved from ancient barter to electronic commerce.
Its main characteristics today are:
- It is based on the law of supply and demand . The offer today is very varied with electronic sales, self-services, large and small surfaces, etc. Demand has changed due to the evolution of consumption habits, the enormous influence of advertising, marketing techniques, etc.
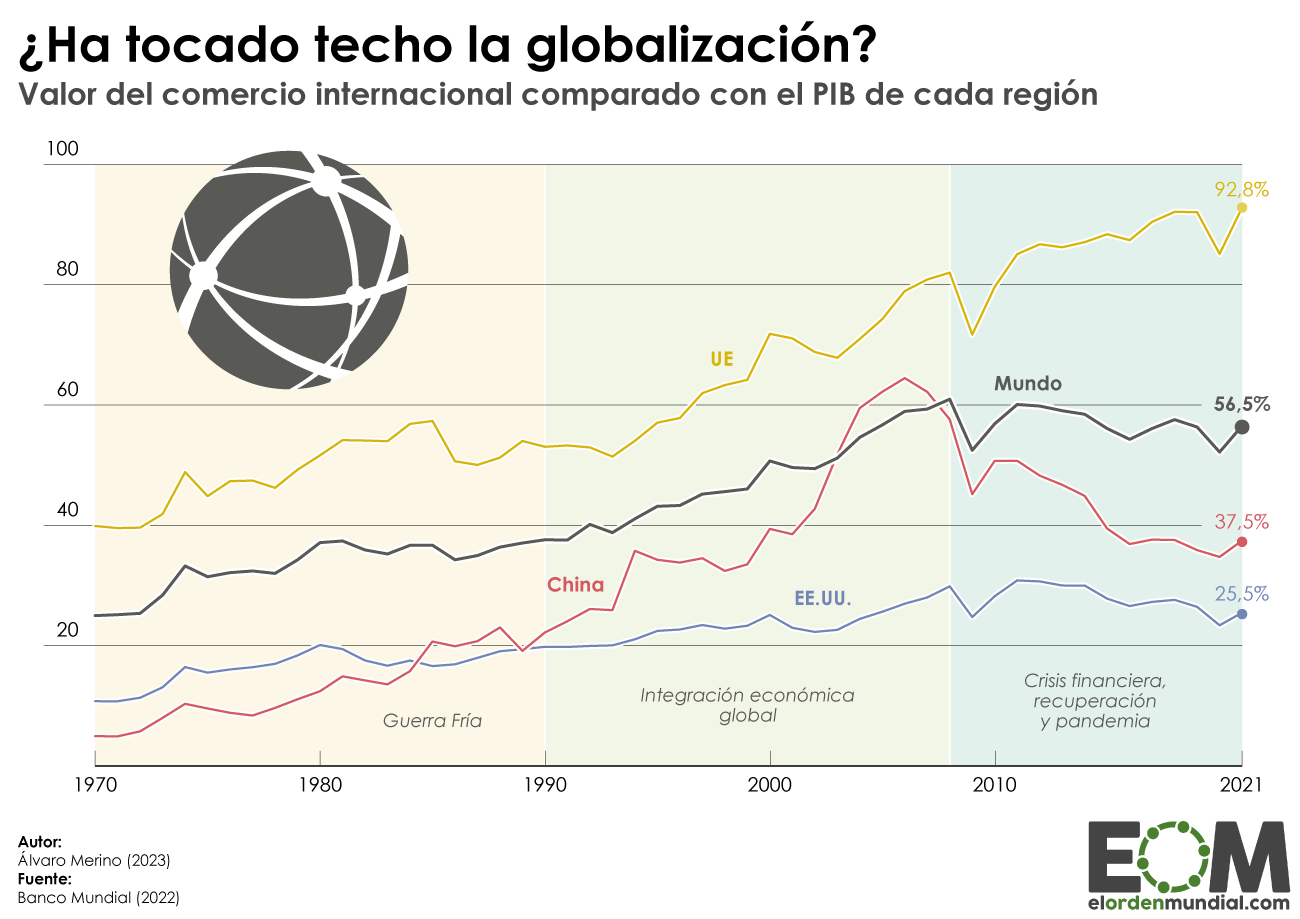
- It has become globalized , creating an enormous global interdependence between countries. Today, large multinationals play a very prominent role in major international trade flows.
- It is concentrated in urban areas and is connected to transport and communications networks. There are large logistics distribution centers, on a global and national scale, that transform spaces.
- It encompasses very diverse activities, from sales at street markets to large multinational purchase transactions.
Internal and external trade
Traditionally, we classify commercial activities according to the space where they take place as internal trade, within a country, and foreign trade, between countries.
Internal trade records all the activities that are carried out within the borders of a country , classifying them as wholesale and retail trade .
Wholesale trade includes all transactions in which you buy directly from producers and sell to retailers or other companies . There are large logistics platforms that store and distribute these products. An example of this wholesale activity would be the distribution of fruit: a company buys large quantities of fruit from the producer and distributes it to central wholesale markets throughout Spain where it is purchased by fruit growers in our neighborhood, village, etc.

Retail is what buys directly from producers or a wholesaler and sells to end consumers . There are different forms of retail:
- Street markets or street markets are temporary places where sellers have their wares on a daily, weekly or temporary basis.
- Traditional commerce , stores located in urban or rural areas that sell directly to the consumer.
- Large commercial areas, such as supermarkets, hypermarkets and shopping centers.
Foreign trade is the exchange of goods and services of a country with the rest of the world . This exchange includes two types of buying and selling:
- Exporting is selling goods or services produced or generated in one country to buyers in any other country or place.
- importing is just the opposite, that is, buying from one country goods or services produced and sold by a different country or region.
Associated with imports and exports we find two economic indicators: the trade balance and the balance of payments .
The trade balance measures the difference between the value of all goods imported and exported by a country. This value can be positive, when exports exceed imports, with the country having a trade surplus . If it is negative, imports exceed exports, we speak of a trade deficit .
The balance of payments not only measures trade, but also all economic and capital transactions of a country with the rest of the world. Like the trade balance, it can be positive or surplus and negative or deficit.
International trade organizations
Globalization and the strong competitiveness of the world market have pushed countries to integrate into international trade organizations to generate synergies that allow them to have positive balances.

The WTO , World Trade Organization , is an international organization that deals with the world-wide rules that regulate trade . Headquartered in Geneva (Switzerland) it was created in 1995 and in 2021 it is made up of 164 members representing 98% of world trade. Among its functions are: the administration of trade agreements, cooperation with other institutions and the forum for negotiations for commercial disputes.
Among the global trade blocs that seek to stimulate the free movement of goods and services that favor the growth of their economies, we highlight:
- The European Union is one of the main global agents of trade, positioned as the second largest importer and exporter worldwide. We have a deficit in the import of goods and a surplus in the export of services.
- The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA or NAFTA in English) signed between the United States, Canada and Mexico, which promotes exchanges between these countries.
- ASEAN , Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
The UN is also present with the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) , created in 1964 for matters related to trade, investments and development. Made up of 195 countries, it supports developing countries to join the globalized economy.
Transport and communications

Transport is the transfer and distribution of people, goods and services between different places . The 19th century saw a first revolution in this sector with the introduction of the steam engine and, since then, technological innovations have been added to it that have increased speed , connectivity and reduced distances .
The areas of travel are land (by rail and road transport), naval (river and sea) and air ( by plane). Let’s now analyze their advantages and disadvantages.
| Means of transport | advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| train | Great load capacity. Low price in the transport of goods. Safe. | High cost of infrastructure construction. Little flexibility. |
| road | Door to door, it’s very flexible. | High cost of construction and maintenance of infrastructures. Traffic congestion. High rates of air pollution. Risk of accidents. |
| ship | High cargo and passenger capacity. Low cost. Safe. | Low travel speed. Impact on the urban fabric of port infrastructures. |
| airplane | High speed allows you to travel long distances in a short time. Safe. | Impact of its infrastructures on the territory. Atmospheric and acoustic pollution. |
The entire set of means of transport is the infrastructure network of a country. These networks are conditioned by physical factors (the relief greatly determines the layout of transport), economic (availability of resources for construction), political (investment decisions in certain areas) and historical . All this forms the density of the network of a space and marks its accessibility , essential for the development of economic activities .
From an environmental point of view, means of transport generate high landscape, acoustic, atmospheric impacts , etc. European governments have begun to bet on more sustainable and connected mobility strategies, based on the massive introduction of mobility technology and the need to ” decarbonise ” the economy .
tourism
Tourism is the movement of people, of a temporary nature , from their place of residence to another space, for leisure reasons . We should not confuse it with migratory movements in which displacement occurs out of necessity or to try to improve living conditions.
This activity has grown exponentially in the last fifty years associated with various social changes :
- The emergence of free and leisure time , a consequence of shorter working days and paid holidays.
- Higher level of income , since the population has more money that they can spend during the holidays and in the enjoyment of their free time.
- The transport revolution , which has allowed more mobility and accessibility, at more affordable prices.
- The consumer society and advertising , which offers us a great variety of activities.
All these factors have promoted that tourism has become a ” mass phenomenon ” with more than 1.4 billion international trips in 2019 according to the WTO (World Trade Organization). A prosperous ” tourism industry ” has developed around it that seeks to satisfy the needs of tourists, from transport infrastructure to hospitality, which facilitate relaxation and enjoyment of leisure time.
International tourism, number of arrivals. World Bank .
This economic subsector of unstoppable growth has also diversified its destinations . People are traveling further and further. What attracts people to visit a place are physical elements , natural (the peaks of the great mountains), human ( the great medieval cathedrals), or a combination of both. Depending on the destination, we talk about different types of tourism :
- Sun and beach , typical of coastal areas in warm and temperate countries.
- Mountain , sport and adventure , which has grown in recent years associated with sports activities such as hiking, climbing or winter sports on snow.
- Cultural , focused on visits to places of historical interest, cities with rich heritage, great exhibitions, etc.
- Religious with pilgrimages to holy places.
- Leisure , visits to theme parks, concerts, etc.
- Health , associated with activities that take care of the body and mind, such as spas.
- Businesses , congresses and professional fairs, which move a huge volume of people.
- Rural , the increasingly high percentage of the urban population means that rural destinations are chosen as elements of leisure.
Is sustainable tourism possible?
The increase in tourism has generated many benefits , but also problems . We analyze below their advantages and disadvantages, as well as the need to develop tourism practices that are more respectful of traditional ways of life and the environment.
| ADVANTAGES | INCONVENIENCES |
|---|---|
| Tourist activity stimulates other economic sectors , brings wealth and benefits the country’s balance of payments . | Mass tourism is associated with holiday packages that are managed by ” tour operators “, who export the profits outside the country. |
| It creates a lot of employment . | The occupations are temporary . |
| It expands and diversifies the cultural contacts of the population. | It expels the population and traditional activities from their usual neighborhoods. |
| Improve the transport and communications network . | It destroys natural landscapes and overcrowds certain areas. |
The UNWTO (World Tourism Organization) declared 2017 the International Year of Sustainable Tourism , which seeks to make tourism practices sustainable from an environmental , economic , social and cultural point of view . It tries to prevent tourists from appropriating and modifying the local heritage and that the economic benefits go to companies that do not come from the local economy.
To achieve this, the UNWTO has established a series of principles that guarantee sustainable tourism; among them, we find:
- Policies that minimize the generation of waste by tourists.
- Adequate management of drinking water and waste water generated by tourist activities.
- More sustainable transport models .
- Involve local communities in conservation activities, but also in economic promotion activities, so as to generate employment and diversify the local economy .
- Achieving sustainable development .
Many natural spaces , rural tourism initiatives and hospitality have joined these principles of sustainability, and have grown the range of activities under this seal of quality.
The tertiary sector in Europe: The tertiaryization of the economy in Europe
The European Union is one of the economic leaders worldwide. Its economic position allows it to compete with the USA , China and Russia . The union of the 27 guarantees its primacy in the world with a gross domestic product (GDP) that represents 22% of the world total .
At the forefront of this economic development is the tertiary sector with a contribution of 70% to the GDP of the union and 73% of the population employed in this sector, according to data from 2019. An enormous variety of economic activities, such as trade, transport, storage, finance, insurance, business and personal services are included in the tertiary sector.

The importance of this sector has increased to become the first generator of employment and wealth in all the countries of the European Union (EU), although with internal differences. While in Germany the service sector accounts for 74% of the employed population, in Romania it is only 48%.
The EU, a leader in world trade
In international trade, the European Union leads the world trade in services; it is also the second largest exporter of goods, behind only China, and the second largest importer behind the USA. The trade balance of goods and services has registered a surplus in recent years, certifying the economic recovery after the 2008 crisis.
At global level, the EU has only one voice in trade policy . Relations with third countries are made through commercial agreements and the existence of tariffs on the import of products are other key elements.
In internal trade , the single market guarantees the free movement of goods, services, capital and people within the EU . In practice, it involves the elimination of borders and technical and legal barriers, which, together with the creation of the euro zone, has been a huge stimulus to economic growth and trade between the countries of the union.
The European commercial policy of the coming years seeks to guarantee security in the circulation of goods and services and sustainability , taking care of the environment and favoring socio-economic development.

The European connection network
One of the fundamental axes for structuring the EU is an infrastructure network that facilitates connectivity between all territories . In the past, there have been many investments in transport with the aim of reducing time and improving the capacity of the roads.
The current transport policy is based on three pillars:
- The commitment to trans-European transport networks ( TEN-T ), networks of common European interest to create corridors for goods and passengers, by road, rail and even have a “single European sky”.
- The creation of multimodal systems and platforms .
- The challenge of reducing emissions .
Europe, favorite destination

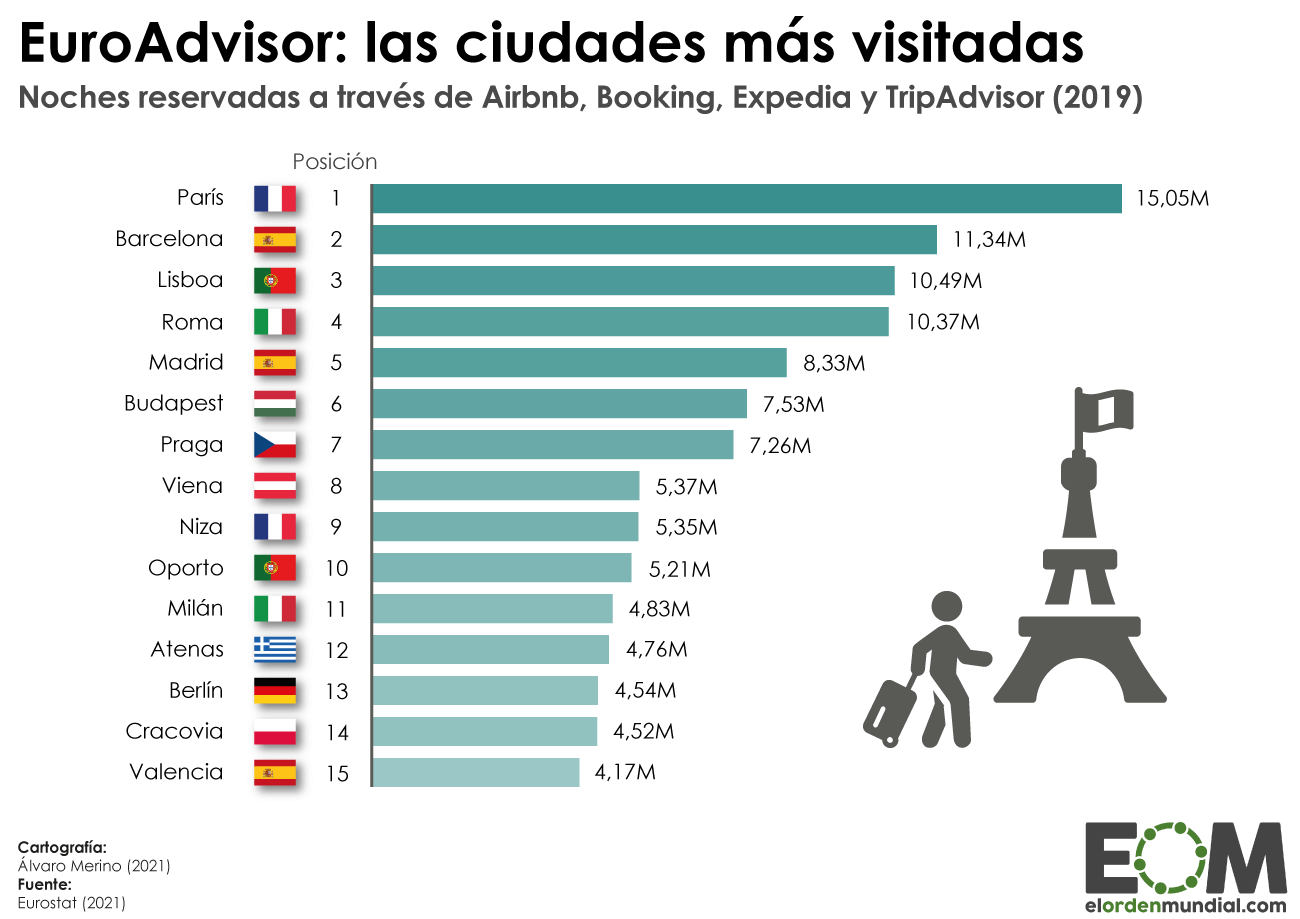
In 2019, 1.5 billion tourists traveled around the world, of which 755 million did so in Europe , 50% of the global total. France is the first destination, followed by Spain, Italy and Germany. Tourism within the EU is a crucial element of the economy , facilitated by the free movement of people, established in the Schengen Treaty, and by the euro .
The tourism policy of the coming years is based on the consolidation of employment , which is highly seasonal, and also on increasing the environmental dimension through the promotion of sustainable, responsible and ethical tourism. Within this policy, some outstanding lines of action have been set:
- The promotion of tourist destinations of excellence ( European destinations of excellence )
- The promotion of tourism for elderly people and disadvantaged groups .
- The creation of a green belt of 6800 kilometers of trails, from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea.
- The promotion of tourist activities among young people ( Discover EU ).
References
- Buxaweb. Tertiary sector
- Miriam Hernando Leal. Itinerary The tertiary sector . Geography and History 3.º ESO Collection “Didactic Itineraries” INTEF.
- National Geographic Atlas
